We independently evaluate the products we review. When you buy via links on our site, we may receive compensation. Read more about how we vet products and deals.
These are the 7 best OTC hearing aids, according to audiologists and testers
Save thousands on these OTC hearing aids selected based on cost, quality, FSA/HSA eligibility and insurance reimbursement
An estimated 48 million Americans suffer from some degree of hearing loss. What's more, a 2015 U.S. Census Bureau report found that 28 million Americans said they believed they could benefit from a hearing aid — but only 1 in 5 people who would benefit from a hearing aid actually used one. At that time, hearing aids were available only by prescription and, often, insurance did not cover their hefty prices. In order to make the market more accessible and competitive, in 2022, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved the sale of over-the-counter (OTC) hearing aids. Now you can buy the best OTC hearing aids at a fraction of the cost of prescription hearing aids through major retailers such as CVS, Amazon and Best Buy.
Jabra Enhance Select 300
Our top pick for the best OTC hearing aid overall
HP Hearing PRO Self-Fitting OTC Hearing Aids
Our top pick for mild-to-moderate hearing loss
Lexie B2 Plus
Our top pick for best for sound customization
Audien ATOM PRO 2
Our top pick for ease of use
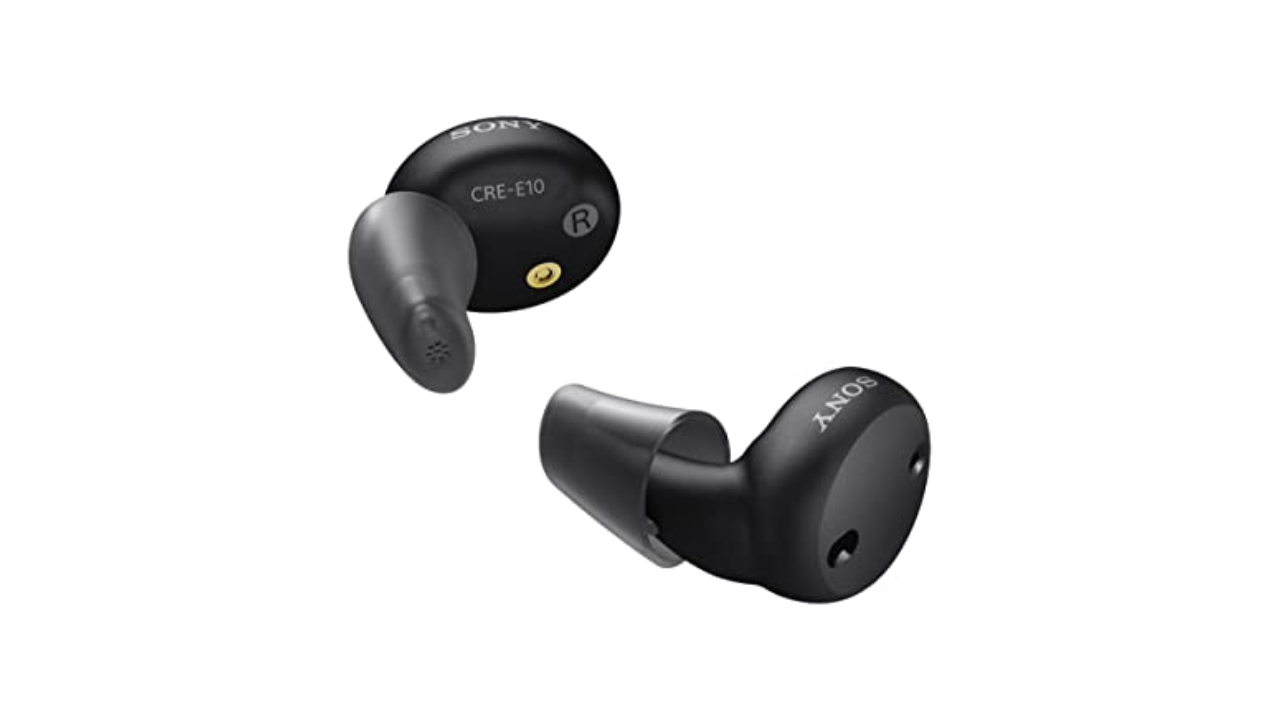
Sony CRE-E10 Self-Fitting OTC Hearing Aids
Our top pick for best sound quality:
Eargo 7
Our top pick for invisible in-ear hearing aid
Lexie Lumen Self-Fitting Hearing Aids
Our top pick for best customer service
The more widespread use of hearing aids could have far-reaching effects. Hearing loss doesn't just affect how you interpret the world through sound. Studies show hearing loss can affect cognitive function and even increase the risk of depression and dementia. Hearing loss also negatively affects physical activity. A recent study found that individuals with some form of hearing loss reported significantly greater difficulty in engaging in moderate or vigorous physical activity compared with those who reported excellent or good hearing.
If you want to explore wearing a hearing aid, there is good news: Hearing aids are more affordable and accessible than ever. Best of all, some of the best hearing aids are so discreet that no one will notice you're wearing one.
To help find the best over-the-counter hearing aids, we spoke with a panel of audiologists, otolaryngologists (ear, nose and throat specialists), physicians and hearing specialists to better understand the difference between prescription and OTC hearing aids, and what to look for in sound quality, comfort, technology and styles. We then researched and tested 20 of the best OTC hearing aids on the market. Here are our top picks for the best over-the-counter hearing aids of 2024.
Table of contents
Best OTC hearing aid overall
Cost: $1,495 - $1,695 | Best for: Mild-to-moderate hearing loss | Covered by Insurance: Reimbursement available | FSA/HSA Eligible: Yes | Style of Fit: Receiver in canal (RIC) | Battery Type: Rechargeable | Remote/App Customization: Yes
The Jabra Enhance Select 300 offers sound quality comparable to prescription devices, thanks to technology that includes a dual-core chip that enables it to differentiate between speech and background noise, automatically adjusting for clarity. The app or an audiologist can fully customize the hearing aids to meet your hearing profile needs. This hearing aid is best for mild-to-moderate hearing loss and has an IP67 rating for water and dust resistance, so it’s suitable for active lifestyles where moisture (rain, sweat, splashes) may be a concern.
As a receiver-in-canal hearing aid, it fits discreetly and securely behind the ear and connects to an invisible wire with a small speaker that fits comfortably in the ear canal, amplifying sound. Its smart microphones and a powerful processor deliver more natural sound in complex situations, while the built-in advanced noise cancellation allows for clearer sound in crowded areas. There's also enhanced spatial sense allowing for increased awareness of sounds coming from the sides and behind.
There are two Select 300 options to choose from:
The premium package — $1,795 — This is a fully customizable hearing aid allowing for remote adjustments from the audiology team plus a three-year warranty and three years of follow-up care.
The basic package — $1,495 — While it carries the same dual-core chip technology, it is a preprogrammed hearing aid that only offers three hearing profiles to choose from.
You'll need a smartphone or tablet to use the hearing aids since you need to make customizations through the app. You can opt into the premium package ($1,795) to have an audiologist remotely make adjustments for you, but you will still need to have access to the app to make adjustments to the settings and pair with your other devices, such as a smartphone or TV, for streaming audio and hands-free calls. Additionally, users without an iPhone 11 or newer may need to purchase the Phone Clip+ accessory to take advantage of hands-free calling.
If you are unsure if you need a hearing aid or if this is the best hearing aid for you, Jabra offers an online hearing test.
- Dual-core chip that automatically adjusts for sound clarity
- App-based customizations to support your hearing profile
- IP67 rating for water and dust resistance
- Hands-free calling available only for iPhone 11 and newer
- Suitable only for mild-to-moderate hearing loss
- Requires smartphone or tablet
Other top OTC hearing aids we recommend for 2024
Cost: $499 | Best for: Mild-to-moderate hearing loss | Covered by Insurance: No | FSA/HSA Eligible: Yes | Style: In-the-ear (ITE) | Remote/App Customization: Yes
The HP Hearing Pro has an earbudlike design that rests inside the ear similar to a pair of wireless earbuds. Notably, this product is the first to receive FDA clearance under a new category of hearing devices called “Self-Fitting Air-Conduction Hearing Aid, Over The Counter.” The self-fitting feature allows you to calibrate your device through the app-based program without a professional hearing test. Note: We still recommend consulting with an audiologist for a proper diagnosis.
The HP Hearing Pro also offers several listening modes for different environments, streaming capabilities and a portable charging case. The battery life lasts approximately eight hours for everyday hearing and five hours for streaming. While this is shorter than the battery life of many other OTC models, this model has the average battery life of standard wireless earbuds.
The company offers a two-year warranty (higher than most), making it a solid choice for those with mild-to-moderate hearing loss seeking an affordable option.
- Simple earbud design
- Automatic calibrations
- Works with Android and iOS
- Available only in one color (black)
- Lower battery life than other models
Cost: $899 | Best for: Mild-to-moderate hearing loss | Covered by Insurance: No | FSA/HSA Eligible: Yes | Style of Fit: Receiver in canal (RIC) | Battery Type: Rechargeable | Remote/App Customization: Yes
We chose the Lexie B2 hearing aid by Bose as our pick for best customization, thanks to the robust app that offers multiple customization features based on your individual hearing profile. You can program the settings of the Lexie B2 Plus hearing aid to meet your specific hearing needs using the app's built-in hearing test. This test helps you find the perfect settings based on your individual hearing profile. The hearing aids have the ability to make hands-free phone calls (iPhone only) and stream music; after all, this is a product created by Bose, a leader in sound quality.
You can also easily connect with a Lexie hearing expert via the app who can offer support via video, chat or phone. While some OTC hearing aid brands give you a set time for free support, Lexie offers ongoing, lifetime support. Customer service is also available seven days a week.
- Free ongoing professional support
- Customer service available seven days a week
- Lifetime support
- Streaming not compatible with Android
- Available only in gray
Cost: $289 | Best for: Mild-to-moderate hearing loss | Covered by Insurance: No FSA/HSA Eligible: Yes | Style: In-the-canal (ITC) | Remote/App Customization: No
When it comes to ease of use out of the box, the Audien Atom Pro 2 has all the basics covered without the extras that can complicate setup. These in-the-canal hearing aids are smaller than previous Audien models to fit more comfortably in your ear. The benefit of its simplistic design is its ease of use. You don't need a smartphone or app to control the volume or programs, which is ideal for those who aren't tech-savvy.
The downside to this is that you're limited in terms of customization. There aren't any preset listening profiles or advanced settings, and you'll have to remove the hearing aids to change the volume. That said, its impressive battery can last up to 24 hours on a single charge.
The Atom Pro 2 also has a UV charging case that eliminates bacteria and keeps your hearing aids clean. The company offers a 45-day money-back guarantee, and you can make a purchase by using your HSA or FSA card.
- Relatively discreet
- No smartphone or app needed
- Battery lasts up to 24 hours
- Lacks advanced customization
- Manual adjustments take longer
Cost: $998 | Best for: Mild-to-moderate hearing loss | Covered by Insurance: No | FSA/HSA Eligible: Yes | Style: In-the-ear (ITE) | Remote/App Customization: Yes
The Sony CRE-E10 hearing aid looks like your average earbuds, and with sound quality to match. The sound profile is richer compared to that of other models, with controls for volume, balance and directionality of sound in the app. These in-the-ear hearing aids are water- and dust-resistant with an IP68 rating, so you can wear it while exercising or in light rain.
You'll need to use the Sony Hearing Control app (available for iOS and Android) to control your hearing aids' settings. This model doesn't have physical buttons for manual control. Instead, you can adjust everything through the app, including fine-tuning for different environments. Unfortunately, you won’t have the same connectivity options for streaming audio with an Android device.
The CRE-E10 hearing aids come with four sizes of silicone tips, a charging case and cleaning accessories. Sony estimates that the batteries last up to 26 hours on a single charge — more than most. You can also use your health savings account (HSA) or flexible spending account (FSA) toward this purchase.
- Water and dust-resistant
- App for adjusting volume and sound settings
- Battery lasts up to 26 hours
- No buttons for manual control
- Not Bluetooth streaming compatible with Android
Cost: $2,490 | Best for: All levels of hearing loss | Covered by Insurance: Yes | FSA/HSA Eligible: Yes | Style of Fit: Completely-in-canal (CIC) | Battery Type: Rechargeable | Remote/App Customization: Yes
The Eargo 7 is a completely-in-canal hearing aid that boasts an almost invisible-to-the-naked-eye design. Its small size and low profile make it a discreet option when aesthetics are a priority. The hearing aid sits deep in the ear canal, so it's less prone to being knocked out of place or falling out. The soft, flexible silicone-petal tips flex to conform to your ear's shape — it includes additional sizes in the box if you need to change it. You can remove the petal tip and mic cap for easy cleaning.
The Eargo app works with the hearing aids for remote adjustments and control. There's no physical volume wheel or buttons, but you can adjust through three sound profiles by tapping your ear (after initial app programming). The app also allows you to change volume, filtering and programs with the touch of a button. If you need help with your Eargos, the app includes video chat support for professional guidance.
One downside is that the Eargo 7 doesn't have Bluetooth connectivity for streaming audio. Still, its automatic sound technology adapts to each environment — transitioning between music, phone calls or conversation. Although it may not be the most affordable option, it includes ongoing customer support and an up to two-year warranty. Plus, some insurance plans may cover part or all of the cost.
- Discreet, virtually invisible design
- Lifetime virtual support
- Self-fitting
- More expensive than other OTC brands
- No Bluetooth streaming
Cost: $699 | Best for: Mild-to-moderate-hearing loss | Covered by Insurance: No | FSA/HSA eligible: Yes | Style: Behind-the-ear (BTE) | Remote/App Customization: Yes
The Lexie Lumen stands out for having many of the same features of the Lexie B2 Plus, including the exceptional lifetime hearing aid support via the app, included with purchase. While this model will cause you to forgo hands-free calls and streaming, it does have a telecoil that functions as an antenna to provide crisp, clean sound directly to your hearing aids. Using the Lexie Remote app, you'll connect via Bluetooth to your hearing aids to change the sound settings and listening profiles according to your personalized hearing test. There are six listening profiles for different situations — Everyday, noisy indoor, outdoor, music, telecoil and companion mic. When it comes to fit, this is a behind-the-ear (BTE) hearing aid that connects to an earpiece via a clear tube. You can choose from five neutral colors: beige, gray, bronze, silver, and metallic black.
Unlike any other manufacturer on this list, hearing aid and general support are available seven days a week via the app with the choice of video, chat or live phone call response. Unfortunately, the batteries aren't rechargeable and need replacing every four to seven days, depending on use.
Lexie offers a 45-day trial period. If you decide they're not for you within that time frame, return the aids for a refund.
- In-app hearing test for personalizing your settings
- 45-day trial period and 1-year warranty
- Customer service available seven days a week
- No streaming or hands-free phone calls
- Batteries need replacing every four to seven days
Factors to consider when buying an OTC hearing aid
Regardless of whether you opt for a prescription or OTC hearing aid, a professional evaluation should be the first step to assess for any underlying medical conditions and determine the appropriate level of amplification needed, said Leigh Smith, clinical audiologist and owner of Florida Audiology Associates.
There are several key factors to consider when purchasing a hearing aid:
Style of hearing aid: There are multiple styles of hearing aids, each of which caters to different aesthetics and functionality.
Behind-the-ear (BTE): These rest behind the ear while a plastic tube directs amplified sound into the ear canal through an ear mold. BTE hearing aids are suitable for most types of hearing loss and are the most visible.
Receiver-in-canal (RIC): RICs are like BTEs but with the speaker or receiver placed inside the ear canal. The size reduction often makes them less visible and more comfortable, and they can provide natural sound quality.
In-the-ear (ITE): Most ITEs are custom-made and fit within the outer ear; ITE aids are easier to handle and are often a top pick due to their discreet profile.
In-the-canal (ITC): Many of these devices are custom molded and fit partly in the ear canal, making them less noticeable than ITE models.
Completely-in-canal (CIC): The most discreet option, CICs fit deep inside the ear canal and are typically custom-fitted to be nearly invisible. They are well-suited for mild-to-moderate hearing loss. However, they may be challenging for users with dexterity issues due to their small size.
Cost: Hearing aids can cost anywhere from a few hundred dollars to several thousand dollars. Some insurance plans may cover hearing devices partially or entirely, and certain models are eligible as an FSA/HSA-approved expense. Consider your budget and insurance, and whether your purchase includes the cost of batteries and accessories.
Prescription or OTC: Prescription hearing aids require a medical evaluation and fitting by an audiologist, while OTC options do not. An OTC model may be suitable if you have mild-to-moderate hearing loss and are comfortable with technology. However, a prescription hearing aid is likely the best option if you have moderate-to-severe hearing loss or prefer professional fitting and support. Also, prescription hearing aids generally come as single devices, while OTC aids come as a pair. If you are experiencing hearing loss in both ears, OTC aids can be a great starting point compared to what two prescription hearing aids would cost.
Self-fitting: Customization of hearing aids to your personal hearing profile (called self-fitting) is not available in all models of hearing aids. Usually, you can customize the settings for your needs by taking a hearing test within the manufacturer's app. Many self-fitting hearing aids come with an option to have an audiologist assist with setup remotely.
Setup: Prescription hearing aids require professional fitting and calibration, while OTC options generally require self-setup. However, some OTC options now offer remote programming and assistance from a hearing professional. Remote access allows you to send data and receive tailored adjustments from an audiologist without an in-person visit.
App pairing: Basic hearing aids use physical buttons to adjust volume and settings, whereas many newer hearing aids offer a companion app for customizing sound profiles and tailoring the amplification level based on your environment. Consider whether you prefer a model with app-pairing capabilities or if standard controls are sufficient.
Bluetooth capabilities: Bluetooth hearing aids that connect to your smartphone are great for streaming music, making hands-free phone calls and streaming TV audio directly from the device, eliminating the need for headphones or an external speaker. If this is a feature you want, ensure that your chosen model has Bluetooth capabilities and is compatible with your smartphone.
Extra features: Many hearing aids offer additional features such as rechargeable batteries, directional microphones, wind noise reduction, extended battery life and advanced noise cancellation. Trial periods, warranty length and professional support are also important to consider.
How we chose
To help find the best OTC hearing aids, we started by interviewing a panel of audiologists, otolaryngologists, physicians and hearing-aid specialists to better understand the difference between prescription and OTC hearing aids, how the two compare in cost, sound and technology, and what to look for in sound quality, comfort, technology and styles. We then researched and tested many of the top-rated OTC hearing aids on the market, narrowing our list according to features, fit, ease of setup and cost.
FAQs
How do I know whether OTC hearing aids are right for me?
Not everyone with hearing loss should consider OTC hearing aids. For those with severe or profound hearing loss, tinnitus, ear infections or drainage, or those who have undergone ear surgery or have structural ear issues, the best course of action is to work with an audiologist.
Smith said that if you opt for OTC hearing aids to save money, you should do the following to ensure safety and efficacy:
Have your hearing tested by a professional to confirm your mild to moderate hearing loss.
Verify the return period of the device in case it doesn’t work properly or isn't a good fit.
Visit a hearing care professional who uses Real Ear Measurement (REM) after the OTC purchase to confirm whether the hearing aids apply appropriate volume based on your hearing test.
If you've already had a hearing evaluation and are confident in the level of amplification, an OTC model can be a cost-effective and convenient option.
How do OTC hearing aids work?
"Hearing aids are designed to not just amplify sound, but to do so in a way that improves speech clarity and understanding," said Amy Sarow, a clinical audiologist with hearing aid comparison service Soundly. The devices consist of several components, including a microphone, amplifier, speaker and battery. The microphone picks up sound from around you and converts it into electrical signals. The amplifier then increases the strength of these signals before sending them to the speaker, which converts them back to sound waves and delivers them into the ear canal. The battery provides power to all of these components.
Modern hearing aids also include advanced technology, such as digital signal processing, noise-reduction algorithms and Bluetooth connectivity. These features can help reduce background noise, improve speech clarity and allow for direct streaming of audio from devices such as smartphones or televisions.
What is the difference between OTC and prescription hearing aids?
The key differences between OTC and prescription hearing aids are cost, level of customization and ongoing professional support. An audiologist needs to conduct a medical evaluation and fitting for prescription hearing aids, while OTC options allow for purchase and customization without a prescription or audiologist.
"Prescription devices are fit precisely by a hearing professional to an individual's audiogram to provide specific amplification tailored to their hearing loss," Sarow said. "For instance, if a person's lower frequency hearing is normal or has mild loss, the hearing aid is programmed to offer minimal amplification in those ranges while providing more volume at higher frequencies where hearing loss is more pronounced.”
However, OTC hearing aids allow users to self-tune their devices via a test or other app-based feature, Sarow said.
"For some individuals who are comfortable with technology, [OTC hearing aids] may provide an alternative to the traditional prescriptive approach to fitting hearing aids," said Dave Fabry, chief hearing health officer with hearing aid manufacturer Starkey. "While this may serve as an entry into hearing aids for those with perceived mild-to-moderate hearing loss, it removes the hearing professional, who is an essential resource for diagnosing and treating hearing loss and for selecting the best technology to meet the individual’s needs," he said.
Prescription hearing aids also offer more ongoing support from a hearing professional to ensure the best fit and performance. Smith cautions that many people using OTC hearing aids are either over- or under-amplified, which can lead to discomfort and even further damage the hearing.
"We believe that the best patient outcomes are achieved when our technology is fitted by a qualified professional," Fabry said.
Are OTC hearing aids as good as prescription hearing aids?
"OTC hearing aids are a good choice for early-stage hearing loss," said Dr. Sreek Cherukuri, a board-certified ear, nose, and throat specialist. "Over-the-counter hearing aids may be ideal for those who want to avoid the often high costs of prescription hearing aids." However, he also notes that OTC models are difficult for users to adjust, leading to potential issues in finding the right amplification level. Cherukuri recommends seeing an audiologist first.
Does insurance or Medicare cover OTC hearing aids?
Medicare does not cover hearing aids. While some Medicare Advantage (Part C) and employer-based insurance plans have hearing aid coverage, for OTC aids, coverage is harder to get without a prescription. Still, coverage varies based on your carrier and plan, so it's best to check with your insurance provider.
How do I know if I need a hearing aid?
If you are experiencing difficulty hearing, especially in social situations or conversations with background noise, get a professional hearing test by an audiologist. "The average individual waits seven to 10 years after they first notice hearing loss to take steps toward addressing their changes in hearing," said Amanda Cooper, a licensed hearing aid specialist. "Hearing loss is correlated with a multitude of health conditions as well as social isolation, which can impact an individual's quality of life." Report any changes in your hearing to a medical professional who can help determine whether a hearing aid is appropriate. "The earlier hearing loss is detected and treated, the better," Cooper added.
Are OTC hearing aids easy to use?
Most OTC hearing aids have a user manual, online tutorials and customer service representatives to help you with setup. After setup, you will still need to fine-tune your OTC hearing aids if you have a particularly loud environment, or during other circumstances not supported by your preset customizations. But once you get the hang of wearing and adjusting your hearing aids, you may wonder why you waited so long to improve your hearing health.
Meet our experts
Dr. Sreek Cherukuri, MD, board-certified ear, nose and throat physician and founder of ClearCast
Amanda Cooper, licensed hearing aid specialist
Dave Fabry, PhD, chief hearing health officer, Starkey
Amy Sarow, Au.D., clinical audiologist and audiology lead at Soundly
Leigh Smith, Au.D., audiologist and owner of Florida Audiology Associates
Anish Thakkar, Au.D., director of audiology at Los Angeles Center for Ear, Nose, Throat and Allergy
Dr. Carissa Wentland, DO, pediatric otolaryngologist