China plans to take 'hack-proof' quantum satellite technology to new heights
China is planning new, cutting-edge quantum communications satellites.
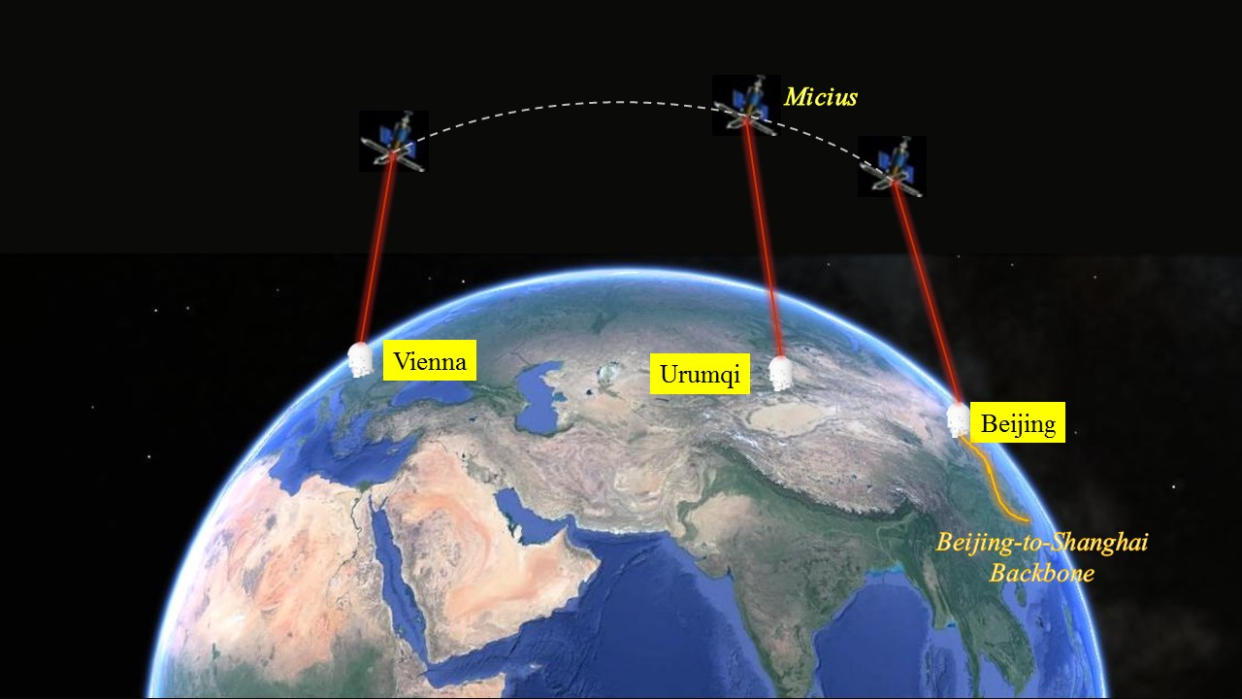
China launched the first dedicated quantum communications satellite, named Micius, in 2016, and has been quietly working on followup missions in the years since. The next satellites will be even more challenging.
"Low Earth orbit quantum key satellite networking and medium- and high-orbit quantum science experimental platforms are the main development directions in the future," Wang Jianyu of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) said Oct. 15 at the third China Space Science Conference, according to a CAS statement.
Related: China launches pioneering 'hack-proof' quantum communications satellite
A QKD ("Quantum Key Distribution") satellite has a photon source that generates individual photons, also known as quantum bits or qubits. These photons are polarized in specific orientations to represent quantum information. The satellite can generate random but entangled pairs of photons, thus creating secret keys, which are distributed to two separate ground stations with detectors to measure the polarization of the incoming photons.
This allows two parties to communicate and encrypt and decrypt data using keys created with quantum properties.
Micius managed to set a new record for the distance over which secure data could be transmitted using quantum means. The satellite sent keys to ground stations in Delingha and Nanshan in China, some 756 miles (1,200 kilometers) apart, and later even farther, sharing data between a site in China and one in Austria.
Placing new quantum satellites in higher orbits, similar to those of GPS satellites, means they will have a greater view of Earth below than does Micius, which orbits at around 310 miles (500 km) above our planet, and will be visible to ground stations for longer periods of time. It also means Chinese scientists and engineers will need to be able to transmit the quantum keys accurately over much greater distances.
To begin sending signals from around 6,200 miles (10,000 km) up, Wang said the challenges include micro-vibration suppression technology needed for spacecraft to send precise optical or laser signals. He did not provide a timeline for the new missions.
RELATED STORIES:
— Europe plans to launch a quantum encryption satellite for ultrasecure communications in 2024
— 10 mind-boggling things you should know about quantum physics
— LIGO gravitational wave detector breaks 'quantum limit' to find deep universe black hole collisions
Wang said that space quantum technology could also bring breakthroughs in areas related to deep space exploration and space gravitational wave detection.
China is not the only country active in this area, which could revolutionize how we transmit sensitive data.
Europe is currently working toward launching a technology demonstration Quantum Key Distribution Satellite (QKDSat), known as Eagle-1, the European Space Agency announced last year.
